What Kinds of Arabic Are There?
By Sarah-Claire Jordan,
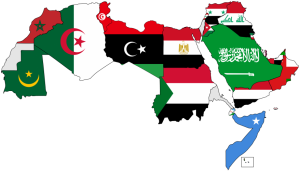 With Arabic being an official language in 24 different countries, you have to at least wonder how many different dialects or varieties of the language exist. Just like the Spanish spoken in Latin America, each country has its own flavor of the language with local slang and even different verb conjugations sometimes. Countries that share a border tend to have similar dialects at least along the border simply due to the constant exchange that goes on there.
With Arabic being an official language in 24 different countries, you have to at least wonder how many different dialects or varieties of the language exist. Just like the Spanish spoken in Latin America, each country has its own flavor of the language with local slang and even different verb conjugations sometimes. Countries that share a border tend to have similar dialects at least along the border simply due to the constant exchange that goes on there.
Continuing with the comparison to Spanish-speaking countries in Latin America, most of the varieties of Arabic are very mutually intelligible, since they are simply dialects of the same language. Here is a breakdown of the different groups of Arabic dialects:
1. Peninsular
Peninsular Arabic includes all of the varieties of Arabic spoken on the Arabian Peninsula. This means the Arabic spoken in Yemen, Oman, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, Kuwait, Bahrain, United Arab Emirates, Iraq, and Jordan. Though this is the area where Arabic originated, the Arabic spoken there does not share very much with Classical Arabic.
2. Maghrebi
This group of Arabic dialects includes all of the dialects and varieties spoken in the Maghreb, the region of North Africa to the west of Egypt. Maghrebi dialects are spoken in Morocco, Tunisia, Libya, and Algeria. They show Berber, Punic, Spanish, French, Italian, Turkish, and English influences.
3. Sudanese
The Sudanese Arabic group includes Chadic, Juba, and Sudanese Arabic. Juba Arabic is used as a lingua franca that developed from a pidgin that was based on Sudanese Arabic. The dialects in this group are considered by some to be the most archaic but purest forms of Arabic, and many accents of Sudanese Arabic speakers are similar to those of Saudi Arabian Arabic speakers.
4. Egyptian
As the name suggests, Egyptian Arabic dialects are spoken in Egypt. They include Egyptian Arabic as well as Sa’idi Arabic, which is spoken mostly around the Egyptian border with Sudan. Speakers of Egyptian Arabic don’t always understand Sa’idi Arabic speakers if they speak a more conservative type of the dialect.
5. Mesopotamian
This Arabic group includes Mesopotamian Arabic and North Mesopotamian Arabic. Since the lingua franca of Mesopotamia was Aramaic, the varieties from that area show some Aramaic influences. It is spoken in Syria, southeastern Turkey, and Iran, as well as within some Iraqi communities who have settled in the region.
6. Levantine
Right next to where Mesopotamian Arabic varieties are spoken, you have the Levantine varieties. They are spoken in Syria, Cyprus, Jordan, Lebanon, and Palestine, and include a total of 8 different dialects. All Levantine Arabic dialects have a unique stress pattern that most other dialects do not have.
7. Andalusian
Though now an extinct group of dialects, Andalusian Arabic included all of the dialects spoken on the Iberian Peninsula during the time when the area was under Muslim rule. As soon as the Moriscos were forced out of the region, these dialects died out. Andalusian Arabic dialects can still be heard in the traditional music of the Andalusia region of Spain.
Alpha Omega Translations is a company focused on translation, interpretation, and desktop publishing services. The translators who work with us have a great understanding of the subtle differences between varieties of any language, be it Arabic, English, Spanish, or others.
For an overview of our translation expertise, visit our editing service page
Category: Foreign Language








